Testicular Cancer in Chattanooga TN
What is testicular cancer?
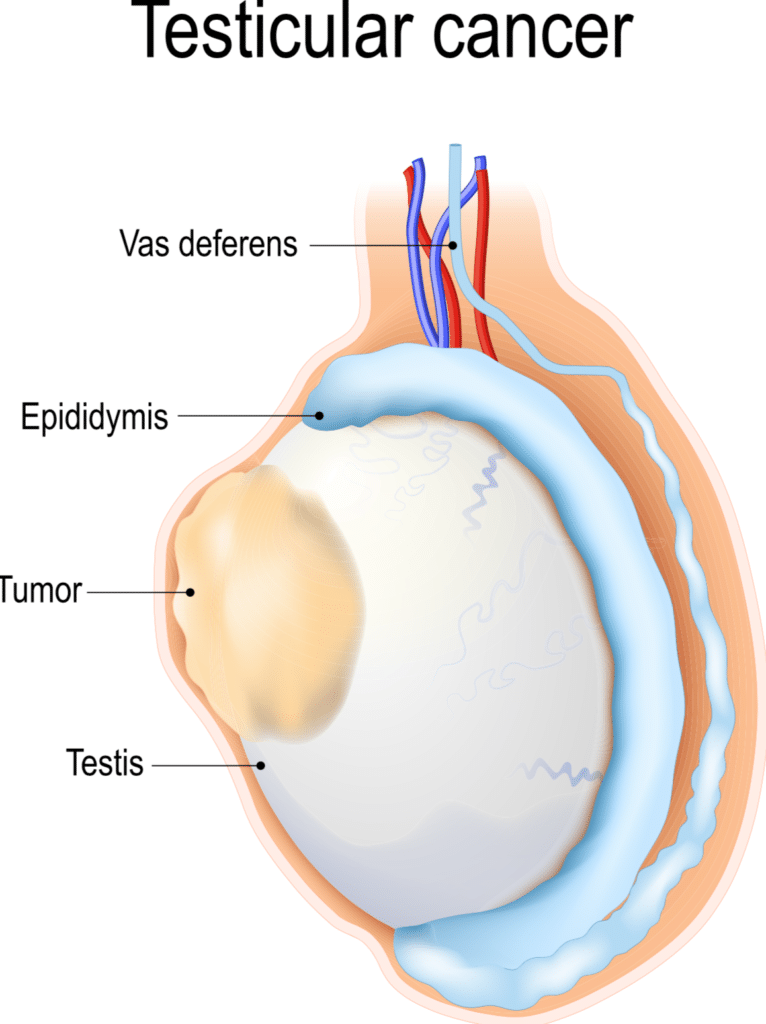
The testicles are glands that produce male sex hormones and sperm. Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in men between the ages of 18 and 35, and yet it is still very rare. It is one of the most treatable cancers, even when it has spread beyond the testicle. If found and treated early, at stage 1 (where the cancer has not spread outside the testicle) it is usually completely curable.
Risk Factors for Testicular Cancer
- Young men with an undescended testicle have a higher risk. This is why self-examination is important. Even after removal of an undescended testicle, there is still a risk of developing testicular cancer of the other testicle.
- Men whose father or brother had testicular cancer are at greater risk.
- A history of abnormal testicular development.
- HIV
- Genetic conditions that cause undeveloped testicles.
- Having had testicular cancer before.
- Note that the majority of men with testicular cancer do not have a history of undescended testicles.
Schedule an Appointment Today
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Testicular Cancer?
- A lump within the testicle
- Swelling or enlarged testicle with or without pain
- A sudden buildup of fluid in the scrotum
- Pain, soreness or ache in the testicle
If a self-exam reveals a lump, swelling or other changes, see your doctor immediately. You should perform testicular self-exam at least every 3 months if you are between the ages of 18 and 35. The earlier you catch a lump, the better your chance for a cure.
How we treat Testicular Cancer in Chattanooga, TN
Your doctor will do a physical exam including your testicles, and take a medical history. You will have blood tests to identify tumor markers- proteins made by the tumor. You may receive an ultrasound to confirm a suspicious lump. You will likely be referred to a urologist who is a surgeon dedicated to managing the testicular disease.
Diagnosis of Testicular Cancer: What’s the next step?
When your diagnosis is confirmed, the next step is to determine whether the cancer has spread. This will require a chest x-ray, CT scan, PET scan, MRI, and lymph node dissection, called a lymphadenectomy, to check if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
Stages of Testicular Cancer
Stage 1- cancer is contained within the testicle
Stage 2- cancer has spread to the lymph nodes
Stage 3- cancer has spread from the lymph to other parts of the body like the liver or lungs
How is Testicular Cancer Treated?
For all stages and types of testicular cancer, the goal of treatment is the surgical removal of the affected testicle. This surgery is called an Inguinal orchiectomy accomplished through a small incision in the groin. The testicle will be removed and examined to check for cancer cells.
Treatment after removal depends on the type of cell involved. Cell type determines how the tumor will behave and respond to treatment.
- The most common cell type is called a seminoma- which responds to both radiation and chemotherapy.
- All other cell types are non-seminomatous tumors. They are more aggressive, and tend to develop earlier in life and spread rapidly. Treatment for these includes observation, surgery and/or chemotherapy.
Treatment Options At Different Stages of Testicular Cancer
If you have stage 1 cancer, removal of the testicle will usually cure the cancer. But, your surgeon will recommend a schedule of follow-up appointments where you will have blood tests, CT scans and other diagnostic procedures to assure the cancer has not returned.
Stages 2 and 3 will need surgery to remove the testicle and the lymph nodes. Lymph node removal is a complex and long operation that can be accomplished by laparoscopic surgery, or open surgery. You may possibly need chemotherapy or radiation after surgery; or removal of tumors that have spread to other parts of the body. Radiation after surgery to remove your testicle may be recommended. Chemotherapy may be your only treatment or recommended before or after lymph node removal surgery.
Schedule an Appointment Today
Patient Testimonial
“The care I received was prompt and thorough. They were good about calling me back and flexible when I needed to reschedule an appointment at the last minute.”
Will Testicular Cancer Treatment Affect My Sexual Or Reproductive Health?
The vast majority of the time cancer is found in only one testicle, and the other will work fine to produce the needed hormones that affect masculinity, sex drive, etc. Removal of a testicle is unlikely to impair sexual function or fertility. However, some men may be concerned about their appearance. They may choose to have an artificial testicle (salt-water filled balloon) implanted in the scrotum. Talk to your surgeon, if you are concerned.
Some treatments, radiation and chemotherapy, can affect your sperm count and the ability to father children. You may be advised to bank your sperm before the testicle is removed or advanced treatments are started.
With the most advanced, new nerve-sparing surgical techniques for lymph node removal can save normal ejaculation function, and is performed on a regular basis by UT Urology surgeons. Our highly qualified and experienced urologists can help avoid ejaculation problems. Experience counts here.
Preventing Testicular Cancer
When you have you periodic checkups, have your testicles examined. Men with risk factors should have more frequent exams. Self- exam is the best way to catch it early.
UT Urology is a regional leader in urology providing care to the people of Chattanooga, Tennessee and Alabama. We offer state-of-the-art diagnostic tools and cutting-edge solutions for your penile cancer. We have multiple fellowship-trained and general urologists who can assist with care, compassion, and excellence.
Schedule a Consultation in Chattanooga, TN
If you have concerns about testicular cancer in Chattanooga, Cleveland, and East Ridge, TN, fill out our contact form and we can answer your questions or call us at (423) 778-5910.
.